SAML
The most important industry standard for Identity Management is the SecurityAssertion Markup Language (SAML). SAML is based on the eXtensible Markup Language (XML) and enables the secure exchange of XML-based authentication messages. In conjunction with Single Sign-On (SSO) systems, SAML especially offers a standardized format for authentication tokens. Authentication and authorization data are defined in SAML Assertions.
SAML Usage
- Single Sign-On (SSO)
- Single Logout
- Identity Federation
Login with SAML
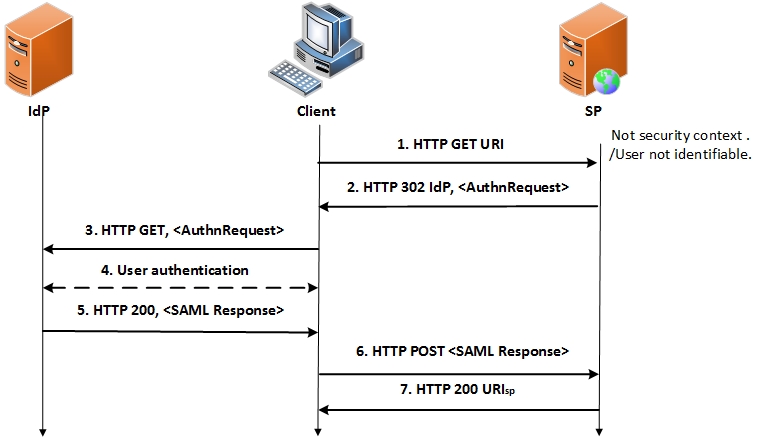
- Service-Provider (SP)-initiated SSO
Here is an example of the AuthnRequst message sent to the IdP:
<samlp:AuthnRequest
xmlns:samlp="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:protocol"
ID="jja.."
Version="2.0"
IssueInstant="2010-12-07T23:15:51Z"
ProtocolBinding="urn:oasis:names.tc:SAML:2.0:bindings:HTTP-Redirect"
ProviderName="google.com"
AssertionConsumerServiceURL="https://www.google.com/a/psosamldemo.net/acs"
/>Here is an example of the Response message sent to the SP:
<samlp:Response ID="pam..." IssueInstant="2010-12-07T23:22:00Z">
<Signature>
<SignedInfo>
<Reference URI="">...</Reference>
</SignedInfo>
<SignatureValue>Em9VX...</SignatureValue>
<Signature>
<samlp:Status>
<samlp:StatusCode Value="urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:status:Success" />
</samlp:Status>
<Assertion ID="kob..." IssueInstant="2003-04-17T00:46:02Z" Version="2.0">
<Issuer>https://www.opensaml.org/IDP </Issuer>
<Subject>
<NameID> demouser </NameID>
<SubjectConfirmation> ... </SubjectConfirmation>
</Subject>
<Conditions NotBefore="2010-12-07T23:17:00Z" NotOnOrAfter="2010-12-07T23:32:00Z"> ...
</Conditions>
<AuthnStatement> … urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:ac:classes:Password …
</AuthnStatement>
</Assertion>
</samlp:Response>The shematic representation of Response message:

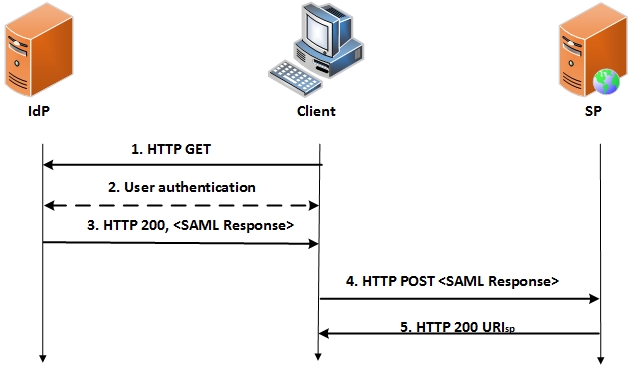
- Identity Provider (IdP)-initiated SSO