Signature Exclusion Attack and XML Signature Wrapping: Difference between pages
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
The | The idea of ''XML Signature Wrapping (XSW)'' is to exploit the separation between SSO Verificator and SSO Processor. In case both logics | ||
have different "views" of the same document, XSW can be applicable. | |||
The goal is to force the SSO Verificator to use different elements than the SSO Processor. | |||
=Attack subtypes= | =Attack subtypes= | ||
There are | There are several options to perform Signature Wrapping depending on the implementation of the verification logic: | ||
*[http://ws-attacks.org/XML_Signature_Wrapping_-_Simple_Context Simple Context] | |||
*[http://ws-attacks.org/XML_Signature_Wrapping_-_Optional_Element Optional Element] | |||
*[http://ws-attacks.org/XML_Signature_Wrapping_-_Optional_Element_in_Security_Header Optional Element in Security Header] | |||
*[http://ws-attacks.org/XML_Signature_Wrapping_-_with_Namespace_Injection With Namespace Injection] | |||
=Prerequisites= | =Prerequisites= | ||
The attacker needs access to a valid token. For this attack to work, the attacker modifies the contents of the token by injecting malicious data without invalidating the signature. | |||
=Target= | =Target= | ||
[[File: | [[File:Target_Verificator_and_Processor1.jpg|centre|600px]] | ||
<br> The attacked Single Sign-On | <br> The attacked Single Sign-On components are marked in red colour. | ||
The attack | The attack targets the discrepancy in the program logic of SSO Verificator and SSO Processor. The latter should extract and forward only exactly the data verified by the former to ''Authorization & Access Management (AAM)''. | ||
=Description= | =Description= | ||
The attacker manipulates his token by injecting malicious contents, for example, the Identity (''I'') of other users. As a result, the attacker can log into arbitrary user accounts and gain unauthorized access to their data. | |||
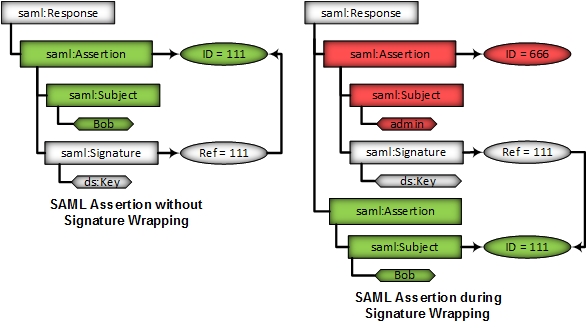
[[File:XML_Signature_Wrapping.jpg|centre]] | |||
<br> The authentication token is signed for a user Bob. Via ''XSW'' the attacker can inject a second ''Assertion'' containing another identity (e.g. admin). The verification logic will verify the Assertion pointed by the Ref, which is valid. The business logic (SSO Processor) will process the injected (malicious) ''Assertion''. | |||
The SSO Verificator will verify the signature based on the contents of the original Assertion, which is selected by ID. However, if the SSO Processor’s program logic automatically processes the first Assertion found within the token, an attacker can bypass the integrity protection and enforce the processing of unverified data on the SaaS-CP. | |||
[[File: | Let us review some different examples of ''Signature Wrapping attack'': <br> | ||
The | [[File:XSW_Example1.jpg|400px]] | ||
[[File:XSW_Example2.jpg|300px]] | |||
[[File:XSW_Example3.jpg|300px]] | |||
<br> In '''Example 1''', the original message with '''ID="111"''' is included into the signature child element. The verification logic finds this element and accepts the signature as correct. The business logic, however, uses the Assertion directly bellow the Root. | |||
<br> In '''Example 2''', the original message with '''ID="111"''' is included into the new '''"666"''' Response as the first child element (i.e., as a sibling of the signature element). The signature logic again finds the original message and accepts it as correct. The business logic uses the '''"666"''' Assertion that was included as the last child element of the new message. | |||
<br> In '''Example 3''', the message contains two top-level elements of type Assertion. The signature logic verifies the signature of the original Assertion '''contained''' in the second Assertion and accepts it as correct. The business logic uses the first Assertion found in the message (i.e., the '''"666"''' Assertion). | |||
=Mitigation / Countermeasures= | =Mitigation / Countermeasures= | ||
The countermeasures depend on the [http://www.sso-attacks.org/XML_Signature_Wrapping#Attack_subtypes attack subtype] in use. | |||
The general approach would be to enhance the interface between the signature verification function and the business logic. In this approach, the signature verification returns some sort of position description of the signed data, next to a Boolean value. | |||
The business logic may then decide if the data about to be processed has been signed or not. | |||
=Practical Examples= | =Practical Examples= | ||
In | In 2014, Mainka et al. analyzed 22 Software as a Service cloud providers and found out, that different frameworks were vulnerable to this attack: Zoho, Clarizen, SAManage, Instructure, AppDynamics, Panopto, TimeOffManager, HappyFox, SpringCM, ScreenSteps Live and LiveHive. | ||
[[Category:Attack_Categorisation_By_Attacker_Model:_Access_to_Valid_Token]] | |||
[[Category:Attack_Categorisation_By_Attacker_Model: | |||
[[Category:Attack_Categorisation_By_Violated_Security_Objective_Access_Control]] | [[Category:Attack_Categorisation_By_Violated_Security_Objective_Access_Control]] | ||
[[Category:Attack_Categorisation_By_Attack_on_IdP/_SP:_Attack_on_SP]] | [[Category:Attack_Categorisation_By_Attack_on_IdP/_SP:_Attack_on_SP]] | ||
| Line 38: | Line 51: | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
C. Mainka, V. Mladenov, F. Feldmann, J. Krautwald, J. Schwenk (2014): Your Software at my Service: Security Analysis of SaaS Single Sign-On Solutions in the Cloud. In The ACM Cloud Computing Security Workshop (CCSW). | C. Mainka, V. Mladenov, F. Feldmann, J. Krautwald, J. Schwenk (2014): Your Software at my Service: Security Analysis of SaaS Single Sign-On Solutions in the Cloud. In The ACM Cloud Computing Security Workshop (CCSW). <br> | ||
[https://hgi.rub.de/media/nds/veroeffentlichungen/2011/10/22/AmazonSignatureWrapping.pdf Juraj Somorovsky, Mario Heiderich, Meiko Jensen, Jörg Schwenk, Nils Gruschka, and Luigi Lo Iacono. All Your Clouds are Belong to us – Security Analysis of Cloud Management Interfaces. In The ACM Cloud Computing Security Workshop (CCSW), October 2011.] <br> | |||
[https://www.nds.rub.de/ | [https://www.nds.rub.de/media/nds/veroeffentlichungen/2012/08/22/BreakingSAML_3.pdf Juraj Somorovsky, Andreas Mayer, Jörg Schwenk, Marco Kampmann, and Meiko Jensen. On breaking saml: Be whoever you want to be. In 21st USENIX Security Symposium, Bellevue, WA, August 2012.] | ||
Revision as of 20:07, 26 January 2016
Introduction
The idea of XML Signature Wrapping (XSW) is to exploit the separation between SSO Verificator and SSO Processor. In case both logics have different "views" of the same document, XSW can be applicable. The goal is to force the SSO Verificator to use different elements than the SSO Processor.
Attack subtypes
There are several options to perform Signature Wrapping depending on the implementation of the verification logic:
Prerequisites
The attacker needs access to a valid token. For this attack to work, the attacker modifies the contents of the token by injecting malicious data without invalidating the signature.
Target
The attacked Single Sign-On components are marked in red colour.
The attack targets the discrepancy in the program logic of SSO Verificator and SSO Processor. The latter should extract and forward only exactly the data verified by the former to Authorization & Access Management (AAM).
Description
The attacker manipulates his token by injecting malicious contents, for example, the Identity (I) of other users. As a result, the attacker can log into arbitrary user accounts and gain unauthorized access to their data.
The authentication token is signed for a user Bob. Via XSW the attacker can inject a second Assertion containing another identity (e.g. admin). The verification logic will verify the Assertion pointed by the Ref, which is valid. The business logic (SSO Processor) will process the injected (malicious) Assertion.
The SSO Verificator will verify the signature based on the contents of the original Assertion, which is selected by ID. However, if the SSO Processor’s program logic automatically processes the first Assertion found within the token, an attacker can bypass the integrity protection and enforce the processing of unverified data on the SaaS-CP.
Let us review some different examples of Signature Wrapping attack:



In Example 1, the original message with ID="111" is included into the signature child element. The verification logic finds this element and accepts the signature as correct. The business logic, however, uses the Assertion directly bellow the Root.
In Example 2, the original message with ID="111" is included into the new "666" Response as the first child element (i.e., as a sibling of the signature element). The signature logic again finds the original message and accepts it as correct. The business logic uses the "666" Assertion that was included as the last child element of the new message.
In Example 3, the message contains two top-level elements of type Assertion. The signature logic verifies the signature of the original Assertion contained in the second Assertion and accepts it as correct. The business logic uses the first Assertion found in the message (i.e., the "666" Assertion).
Mitigation / Countermeasures
The countermeasures depend on the attack subtype in use. The general approach would be to enhance the interface between the signature verification function and the business logic. In this approach, the signature verification returns some sort of position description of the signed data, next to a Boolean value. The business logic may then decide if the data about to be processed has been signed or not.
Practical Examples
In 2014, Mainka et al. analyzed 22 Software as a Service cloud providers and found out, that different frameworks were vulnerable to this attack: Zoho, Clarizen, SAManage, Instructure, AppDynamics, Panopto, TimeOffManager, HappyFox, SpringCM, ScreenSteps Live and LiveHive.
References
C. Mainka, V. Mladenov, F. Feldmann, J. Krautwald, J. Schwenk (2014): Your Software at my Service: Security Analysis of SaaS Single Sign-On Solutions in the Cloud. In The ACM Cloud Computing Security Workshop (CCSW).
Juraj Somorovsky, Mario Heiderich, Meiko Jensen, Jörg Schwenk, Nils Gruschka, and Luigi Lo Iacono. All Your Clouds are Belong to us – Security Analysis of Cloud Management Interfaces. In The ACM Cloud Computing Security Workshop (CCSW), October 2011.
Juraj Somorovsky, Andreas Mayer, Jörg Schwenk, Marco Kampmann, and Meiko Jensen. On breaking saml: Be whoever you want to be. In 21st USENIX Security Symposium, Bellevue, WA, August 2012.
- Pages with broken file links
- Attack Categorisation By Attacker Model: Access to Valid Token
- Attack Categorisation By Violated Security Objective Access Control
- Attack Categorisation By Attack on IdP/ SP: Attack on SP
- Attack Categorisation By Attacked Single Sign-On Component: Verificator
- Attack Categorisation By Attack Spreading:Conceptual Flaws
- Attack Categorisation By Attack on SAML